Forensics
Beginner to Mastery
Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program
Comprehensive training in digital forensics and cyber investigations.
Hands-on projects simulating real-world cybercrime scenarios.
Practical exposure to evidence collection, memory analysis, and OS forensics.
Curriculum aligned with latest tools, techniques, and legal frameworks.

Course Duration
400 Hours
Next Batch
23 November 2025
Course Material
Live. Online. Interactive.
Expert guidance and mentorship for building industry-ready skills.

KEY HIGHLIGHTS OF ADVANCED CYBER INVESTIGATION AND FORENSICS SPECIALIST PROGRAM PROGRAM
- Weekly sessions with industry professionals
- Dedicated Learning Management Team
- 400 hours of hands-on learning experience
- Over 138 hours live sessions spread across 06 months
- 138 hours of self-paced Learning
- Learn from Industry Experts.
- More than 10+ industry-related projects and case studies
- One-on-One with Industry Mentors
- 24*7 Support
- Dedicated Learning Management Team
- 1:1 Mock Interview
- No-Cost EMI Option
- Designed for both working professionals and fresh graduates
- High Demand and Career Opportunities
- Competitive Edge and Innovation
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
WHY JOIN ADVANCED CYBER INVESTIGATION AND FORENSICS SPECIALIST PROGRAM PROGRAM?
Comprehensive Curriculum
Covers digital forensics from fundamentals to advanced areas like memory forensics, network forensics, malware analysis, and incident response.
Practical Experience
400+ hours of hands-on learning with 138+ live sessions, self-paced learning, and real-world capstone projects.
Industry-Standard Tools
Gain expertise in tools like FTK Imager, Volatility, Wireshark, Cyber Triage, Autopsy, and Cellebrite.
Expert Mentorship
Learn directly from IIT faculty, IIM/NIT experts, and seasoned industry professionals with real-world experience.
UPCOMING BATCH:
23 November 2025

SkillzRevo Solutions
30 MINUTE MEETING
Web conferencing details provided upon confirmation.
Corporate Training, Enterprise training for teams
Batch schedule
| Batch | Batch Type |
|---|---|
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | Full-Time |
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | Part-Time |
Regional Timings
| Batch | Batch Type |
|---|---|
| IST (India Standard Time) | 09:00 PM–12:00 AM |
| Bahrain, Qatar, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia | 06:30 PM–09:30 PM |
| UAE / Oman | 07:30 PM–09:00 PM |
Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program OVERVIEW
The program is efficiently designed to equip aspiring professionals with significant knowledge, practical expertise and experience to flourish in the changing field of digital forensic and the reaction of the event. The course spreads a comprehensive spectrum of subjects starting with basic concepts in digital forensic and moving into special areas such as memory forensic, network forensic, malware analysis and comprehensive event reaction strategies. The program ensures a strong learning experience, combining the theoretical understanding with the real -world application, and prepares individuals for a successful career in the rapidly developed field of cyber security and digital investigation.
ENROLL NOW & BOOK YOUR SEAT AT FLAT 50% WAIVER ON FEE
Enroll Now →Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program Objectives
The course is designed to provide participants with a wide understanding of digital forensic and event reaction. It includes major concepts such as evidence handling, legal ideas and forensic investigation life cycle. Participants will achieve practical skills in preserving and collecting digital evidence, while Windows and Linux will master the system and OS forensic for the atmosphere. The program also delays memory forensic, network forensic and log analysis to identify and investigate potential security threats. The learners will develop expertise in malware analysis, event reaction and clear, legally making sound forensic reports. Through the hands-on Capstone projects, the participants will apply their skills to the real-world landscapes, preparing them for a successful career in digital forensic, cyber security and reaction to the event.
Enroll Now →Why Learn Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program ?
Master Digital Forensics Principles
Understand core concepts such as evidence handling, the forensic investigation lifecycle, and methodologies used in modern digital forensics.
Collect and Analyze Digital Evidence
Develop skills to acquire and examine evidence from Windows, Linux, mobile, memory, and cloud-based systems.
Advance Incident Response Skills
Learn to perform incident response and malware analysis, identify attack vectors, and implement effective recovery strategies.
Utilize Industry-Leading Tools
Gain hands-on experience with forensic tools and techniques to uncover hidden data, trace cyber incidents, and support legal investigations.
Develop Professional Forensic Reporting
Build expertise in creating clear, concise, and comprehensive forensic reports tailored for both technical and non-technical audiences.
Gain Real-World Experience
Engage in practical projects, labs, and case studies simulating real cybercrime scenarios to prepare for industry challenges.
Program Advantages
Gain hands-on experience with industry-standard tools like FTK Imager, Volatility, and Cyber Triage.
Learn from experienced professionals in digital forensics, cybersecurity, and incident response.
Engage in practical labs and real-world case studies for deeper understanding.
Explore comprehensive topics like evidence collection, Windows and Linux forensics, memory analysis, and cyber law.
Work on hands-on projects analyzing cyber-attacks, performing malware analysis, and simulating corporate cyber incidents.
Flexible learning through a mix of live sessions, recorded materials, and self-paced assignments.
Understand global and regional legal frameworks, data privacy regulations, and the chain of custody.
Ensure compliance with legal standards for handling digital evidence.

Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program program Certifications
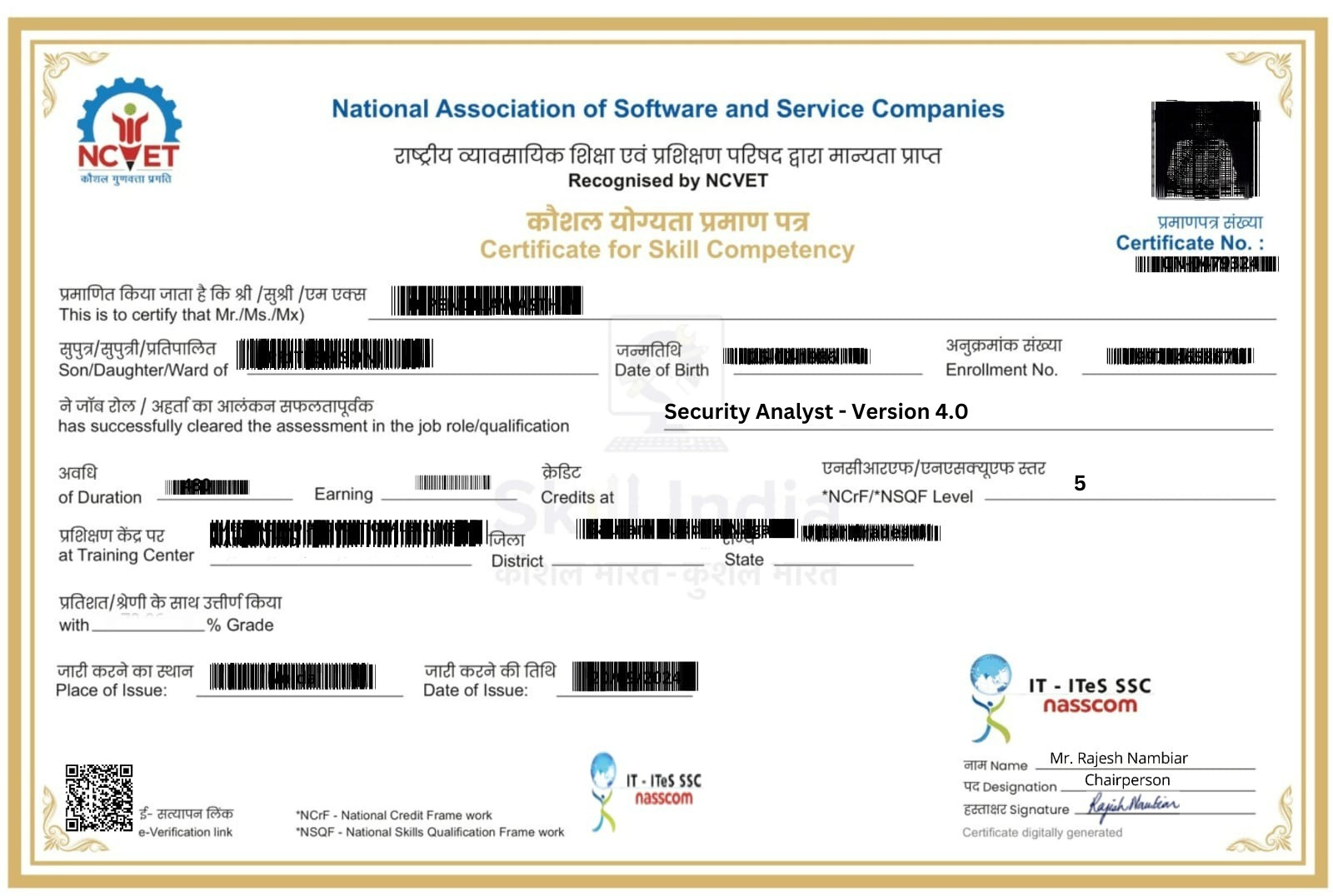
Nasscom

Course Completion

Project Completion
Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program Curriculum
Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program Skills Covered
Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program Tools Covered

Advanced Cyber Investigation and Forensics Specialist Program Program Benefits

CAREER OPPORTUNITIES AFTER THIS COURSE
Incident Response Specialist Salary Range
Min
$500,000
Average
$900,000
Max
$1,500,000

MASTER DIGITAL FORENSICS WITH REAL-WORLD PROJECTS
Hands-on Capstone Projects with Real Data
Practical Labs and Case Studies
Guided by IIT Faculty & Industry Experts
Simulate Real Cybercrime Investigations
Capstone Projects of this Program
Job Obligation After This Course
WE CAN APPLY FOR JOBS IN
Conduct digital forensic investigations to collect, analyze, and preserve electronic evidence.
Identify, analyze, and mitigate cyber threats and incidents across networks and systems.
Perform memory, network, and malware analysis to assess the scope of cyber-attacks.
Prepare detailed forensic reports for technical teams, management, and legal proceedings.
Collaborate with law enforcement agencies, legal teams, and cybersecurity professionals during investigations.
Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and legal standards while handling digital evidence.
Use forensic tools like FTK Imager, Volatility, Cyber Triage, and Wireshark for evidence analysis.
Develop and implement incident response strategies to contain and minimize cyber risks.
Stay updated with the latest cyber threats, attack techniques, and forensic tools to remain effective in investigations.
Companies Hiring for this Course
















































































































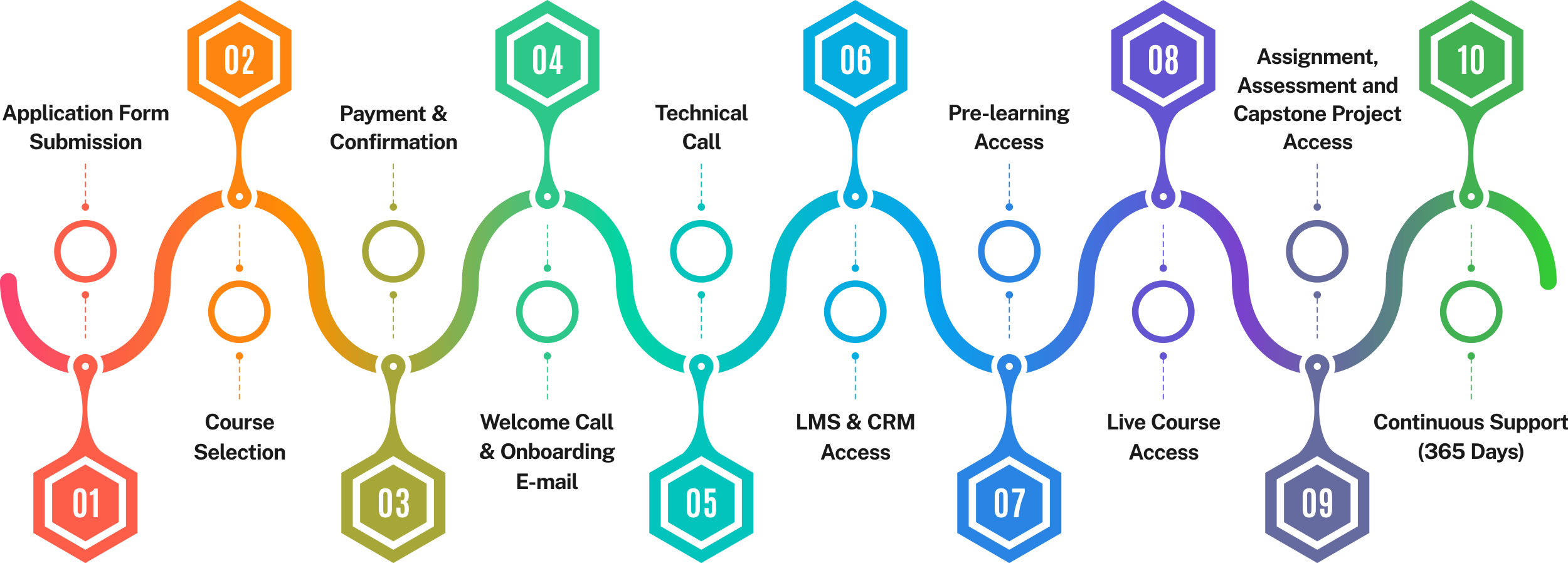
Admission Process
The application process consists of three simple steps. An offer of admission will be made to selected candidates based on the feedback from the interview panel. The selected candidates will be notified over email and phone, and they can block their seats through the payment of the admission fee.
Course Fees & Financing
We partnered with financing companies to provide competitive finance options at 0% interest rate with no hidden costs.


UPCOMING BATCHES/PROGRAM COHORTS
| Batch | Date | Time (IST) | Batch Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | 23 November 2025 | 9 PM to 12 AM | Batch 1 |
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | 30 November 2025 | 9 PM to 12 AM | Batch 2 |
COMPARISON WITH OTHERS
| Feature | Our Course | COMPETITOR A | COMPETITOR B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curriculum Scope | Comprehensive: Python, ML, DL, NLP, CV, Generative AI | Basic ML and DL focus | General AI with less focus on Generative AI |
| Hands-On Experience | Extensive practical projects with tools like GPT, DALL-E 2 | Limited practical projects | Hands-on projects mainly in traditional AI |
| Advanced Tools | GPT, DALL-E 2, Midjourney, Hugging Face, Transformers, GANs, RAG, LangChain | Focus on traditional ML frameworks | Emphasis on standard ML and AI tools |
| Instructor Expertise | Experienced professionals with industry and research background | Mix of industry and academic instructors | Primarily academic-focused instructors |
| Real-World Applications | Emphasis on real-world problem-solving and innovation | Mostly theoretical applications | General applications with less focus on innovation |
| Career Support | Strong focus on career advancement and networking | Basic career services | Limited career support and networking opportunities |
| Networking Opportunities | Connect with peers and industry leaders | Limited networking events | Few networking opportunities |
| Certification Value | Recognized certification for advanced AI roles | Standard certification | General certification with less industry recognition |