Cyber Security
Beginner to Mastery
Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics
Comprehensive, industry-relevant curriculum
Hands-on projects and real-world case studies
Expert-led sessions with practical insights
Career support and job assistance

Course Duration
250 Hours
Next Batch
23 November 2025
Course Material
Live. Online. Interactive.
Access to learning resources and tools
Certification upon successful completion

KEY HIGHLIGHTS OF MASTERING IN CYBER SECURITY & FORENSICS PROGRAM
- Weekly sessions with industry professionals
- Dedicated Learning Management Team
- 900 hours of hands-on learning experience
- Over 320 hours live sessions spread across 13 months
- Total No of Weeks 52
- Duration of Course: 900 Hours
- Pre-Learning Material: 70 Hours
- Offline/Online Live Training: 380 Hours
- Video Recordings of Lectures: 320 Hours
- Capstone Project Discussion & Doubt Clearing Session: 30 Hours
- 1:1 Mock Interview
- No-Cost EMI Option
- Designed for both working professionals and fresh graduates
- High Demand and Career Opportunities
- Competitive Edge and Innovation
- Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
WHY JOIN MASTERING IN CYBER SECURITY & FORENSICS PROGRAM?
Hands-On Learning
Work with leading tools like Metasploit, Burp Suite, and Wireshark to build real-world cybersecurity expertise.
Industry-Relevant Skills
Stay competitive with up-to-date cybersecurity expertise.
Real-World Scenarios
Engage in real-time simulations, penetration testing, and forensic investigations to prepare for actual security challenges.
Adapt to the Future of Cybersecurity
Stay ahead in a fast-evolving industry by mastering the latest cybersecurity trends and techniques.
UPCOMING BATCH:
23 November 2025

SkillzRevo Solutions
30 MINUTE MEETING
Web conferencing details provided upon confirmation.
Corporate Training, Enterprise training for teams
Batch schedule
| Batch | Batch Type |
|---|---|
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | Full-Time |
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | Part-Time |
Regional Timings
| Batch | Batch Type |
|---|---|
| IST (India Standard Time) | 09:00 PM–12:00 AM |
| Bahrain, Qatar, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia | 06:30 PM–09:30 PM |
| UAE / Oman | 07:30 PM–09:00 PM |
Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics OVERVIEW
Our cyber security program is a broad, hand learning experience that is designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge required to flourish in the sometimes-developed area of cyber security. The course includes a wide range of essential subjects including moral hacking, digital forensic, event reaction and security regime. Through the study of practical simulation and real-world cases, you will gain experience with industry-standard devices and techniques, which will prepare you to deal with modern cyber threats effectively.Whether you are an early or experienced professional to enhance your skills, it provides a structured approach to learning the program that ensures both depth and width in cyber security concepts. You will be directed through fundamental concepts and advanced functioning, which gives you the necessary expertise to detect, prevent and respond to safety events. By the end of the program, you will be well prepared to make a career in cyber security and make a meaningful contribution to the conservation of digital assets.
ENROLL NOW & BOOK YOUR SEAT AT FLAT 50% WAIVER ON FEE
Enroll Now →Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics Objectives
The program is designed to provide extensive knowledge and practical experience in cyber security, moral hacking and information protection. It covers major topics such as network safety, danger management and vulnerability evaluation, while also in advanced areas such as penetration testing, malware analysis and digital forensic. Students will learn the essential tools and techniques used by cyber security professionals, including vulnerability scanning, encryption methods and event reaction strategies. With hands-on labs, case studies and real-world simulation, the program equips participants with the skills required to assess and reduce security risks in various environments. This is ideal for individuals who are looking to start or pursue their career in cyber security, IT security or moral hacking.
Enroll Now →Why Learn Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics ?
Growing Cyber Threats
The increasing complexity of cyberattacks makes cybersecurity expertise crucial for individuals and organizations.
Comprehensive SkillSet
Gain hands-on experience in ethical hacking, penetration testing, digital forensics, SOC operations, and incident response.
Industry-Relevant Knowledge
Learn about risk management, compliance frameworks, cloud security, and blockchain security to secure modern IT infrastructures.
High Demand for Cybersecurity Professionals
Organizations worldwide are actively seeking skilled cybersecurity experts to protect their digital assets.
Lucrative Career Opportunities
Unlock high-paying roles such as Cybersecurity Analyst, Ethical Hacker, Digital Forensic Investigator, and Security Consultant.
Cross-Industry Applications
Cybersecurity skills are essential across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, government, and IT.
Program Advantages
Industry-driven course ensuring up-to-date, in-demand knowledge and skills.
Learn through real-world scenarios, simulations, and live projects to tackle cybersecurity challenges.
Learn from certified professionals offering insights beyond theoretical knowledge.
Covering Ethical Hacking, Penetration Testing, Digital Forensics, and more.
Access career services like mentorship, resume building, and job placement assistance.
Flexible online learning accessible to both professionals and fresh graduates.
Access course materials anytime, learn at your own pace.
Gain hands-on experience with tools like Splunk, Nessus, Burp Suite, and Metasploit.
Job-ready focus with practical skills and industry certifications for competitive cybersecurity roles.
Earn a globally recognized certification to boost credibility and career prospects.

Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics program Certifications
Nasscom

Course Completion

Project Completion
Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics Curriculum
Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics Skills Covered
Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics Tools Covered










Mastering in Cyber Security & Forensics Program Benefits

CAREER OPPORTUNITIES AFTER THIS COURSE
Incident Response Specialist Salary Range
Min
$105,000
Average
$119,000
Max
$133,000

Projects that you will Work On
Practice Essential Tools
Designed By Industry Experts
Get Real-world Experience
Capstone Projects of this Program
Job Obligation After This Course
WE CAN APPLY FOR JOBS IN
Investigate cyber-crimes and analyze digital evidence to uncover attack sources and gather forensic data.
Respond to security breaches, contain threats, and recover compromised systems.
Perform ethical hacking to identify vulnerabilities and help organizations strengthen their security posture.
Monitor network traffic and system logs, detect threats, and prevent security incidents.
Design and implement security systems, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS).
Recover and secure data from compromised or damaged systems using forensic tools.
Manage security operations, monitor for threats, and ensure the security of enterprise networks.
Advise businesses on best practices for protecting data, systems, and networks from cyber threats.
Companies Hiring for this Course
















































































































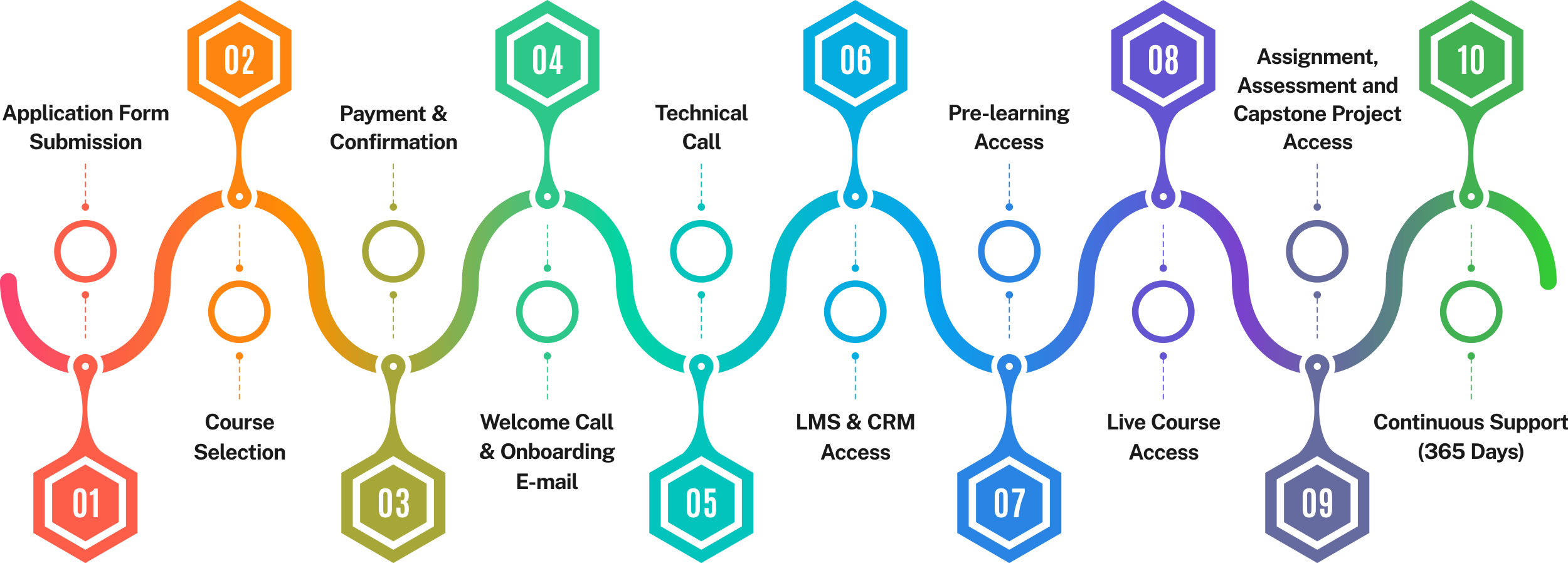
Admission Process
The application process consists of three simple steps. An offer of admission will be made to selected candidates based on the feedback from the interview panel. The selected candidates will be notified over email and phone, and they can block their seats through the payment of the admission fee.
Course Fees & Financing
We partnered with financing companies to provide competitive finance options at 0% interest rate with no hidden costs.


UPCOMING BATCHES/PROGRAM COHORTS
| Batch | Date | Time (IST) | Batch Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | 23 November 2025 | 9 PM to 12 AM | Batch 1 |
| Online Live Instructor Led Session | 30 November 2025 | 9 PM to 12 AM | Batch 2 |
COMPARISON WITH OTHERS
| Feature | Our Course | COMPETITOR A | COMPETITOR B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | 52 Weeks (900 Hours) | 5 Days or Self-Paced | 90 Days (Self-Paced) |
| Learning Format | Live Online + Self-Paced + Capstone Projects | Self-Paced + InstructorLed Labs | Self-Paced + Hands-On Labs |
| Hands-On Labs | Yes (300+ Hours) | Limited Practical Exposure | Limited Practical Exposure |
| Tools Covered | Wireshark, Metasploit, Nmap, Burp Suite, SIEM, etc. | Wireshark, Nessus, Metasploit, Kali Linux coverage | General Theoretical Coverage |
| Tools Covered | Wireshark, Metasploit, Nmap, Burp Suite, SIEM, etc. | Wireshark, Nessus, Metasploit, Kali Linux coverage | General Theoretical Coverage |
| Career Support | Resume, Mock Interviews, Job Assistance | Exam Preparation Only | Exam Preparation Only |
| Best For | Beginners to Advanced – Comprehensive Learning | Beginners to Intermedia to – Focused on Ethical Hacking | Advanced Professionals – Red Teaming |
| Job Roles After Completion | Cybersecurity Analyst, Pen Tester, Forensic Investigator, SOC Analyst, Cloud Security Specialist | Ethical Hacker, Security Analyst | Red Team Specialist, Exploit Developer, Pen Tester |